The Islamic State group still commands between 5,000 and 7,000 members across its former stronghold in Syria and Iraq and its fighters pose the most serious terrorist threat in Afghanistan today, U.N. experts said in a report circulated Monday.
The experts monitoring sanctions against the militant group, also known by its Arab acronym Daesh, said that during the first half of 2023 the threat posed by IS remained “mostly high in conflict zones and low in non-conflict areas.”
But the panel said in a report to the U.N. Security Council that “the overall situation is dynamic,” and despite significant losses in the group’s leadership and reduced activity in Syria and Iraq, the risk of its resurgence remains.
“The group has adapted its strategy, embedding itself with local populations, and has exercised caution in choosing battles that are likely to result in limited losses, while rebuilding and recruiting from camps in the northeast of the Syrian Arab Republic and from vulnerable communities, including in neighboring countries,” the experts said.
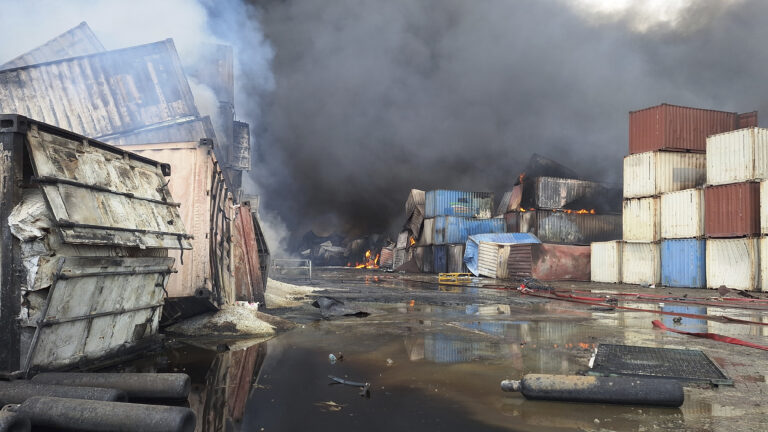
The Islamic State group declared a self-styled caliphate in a large swath of territory in Syria and Iraq that it seized in 2014. It was declared defeated in Iraq in 2017 following a three-year battle that left tens of thousands of people dead and cities in ruins, but its sleeper cells remain in both countries.
Despite sustained counter-terrorism operations, Daesh continues to command between 5,000 and 7,000 members across Iraq and Syria, “most of whom are fighters,” though it has reduced its attacks deliberately “to facilitate recruiting and reorganization,” the experts said.
In northeast Syria, approximately 11,000 suspected Daesh fighters are being held in facilities of the Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces, which have played a prominent role in the fight against IS, the panel said. The fighters include more than 3,500 Iraqis and approximately 2,000 from almost 70 nationalities, it said.
Northeast Syria is also the site of two closed camps – al-Hol and Roj – where the experts said some 55,000 people with alleged links or family ties to IS are living in “dire” conditions and “significant humanitarian hardship.”
Approximately two-thirds of the population are children including over 11,800 Iraqis, nearly 16,000 Syrians and over 6,700 youngsters from more than 60 other countries, the experts said.
The panel quoted one unnamed country as saying Daesh has maintained its “Cubs of the Caliphate” program, recruiting children in the overcrowded al-Hol camp. In addition, more than 850 boys, some as young as 10, were in detention and rehabilitation centers in the northeast, the experts said.
In Afghanistan, the panel said U.N. members assess the Islamic State group poses the most serious terrorist threat to the country and the wider region. IS has reportedly increased its operational capabilities and now has an estimated 4,000 to 6,000 fighters and family members in Afghanistan, it said.
In Africa, on a positive note, the experts said the deployment of regional forces in Mozambique’s Cabo Delgado province disrupted the IS affiliate, and regional countries estimate it now has 180-220 male fighters with battlefield experience, down from 280 previously.
In the east, the experts said several countries expressed concern that terrorist groups like Daesh could exploit political violence and instability in conflict-wracked Sudan.
And some countries assess that the Daesh affiliate in Africa’s Sahel “has become increasingly autonomous and had played a significant role in the escalation of violence in the region, alongside other terrorist groups,” they said, pointing to increased IS attacks on several fronts in Mali and to a lesser extent in Burkina Faso and Niger.
(AP)