Increases in China’s defense budget have been “appropriate and reasonable” and are aimed at meeting “complex security challenges,” a spokesperson for the country’s rubber-stamp parliament said Saturday.
Wang Chao gave no indication of whether the rate of increase to be announced Sunday at the opening of the National People’s Congress’s annual session would be above or below last year’s 7.1%.
But he said the defense budget has remained stable as a share of GDP and that China’s military modernization “will not be a threat to any country.”
“On the contrary, it will only be a positive force for safeguarding regional stability and world peace,” Wang told reporters at a news conference.
“The increase in defense spending is needed for meeting the complex security challenges and for China to fulfill its responsibilities as a major country,” he said.
“China’s defense spending … is lower than the world average and the increase is appropriate and reasonable,” Wang said.
China spent 1.7% of GDP on its military in 2021, according to the World Bank, while the U.S., with its massive overseas obligations, spent a relatively high 3.5%.
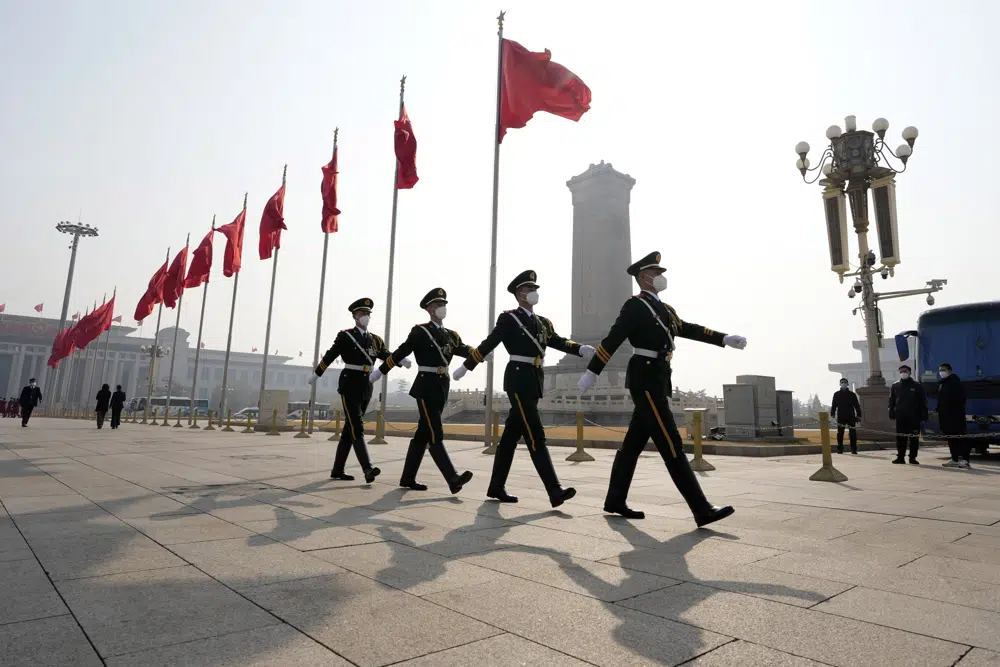
China budgeted 1.45 trillion yuan (then $229 billion) for last year — roughly double the figure from 2013. Consistent annual increases for more than two decades have allowed the 2 million-member People’s Liberation Army to increase its capabilities across all categories.
Along with the world’s biggest standing army, China has the world’s largest navy and recently launched its third aircraft carrier. It boasts a massive stockpile of missiles, along with stealth aircraft, bombers capable of delivering nuclear weapons, advanced surface ships and nuclear powered submarines.
China has already established one foreign military base in the Horn of Africa nation of Djibouti and is refurbishing Cambodia’s Ream Naval Base that could give it at least a semi-permanent presence on the Gulf of Thailand facing the disputed South China Sea.
The modernization effort has prompted concerns among the U.S. and its allies, particularly over Taiwan, the self-governing island democracy that China claims as its territory to be brought under its control by force if necessary.
That has prompted a steady flow of weapons sales to the island, including ground systems, air defense missiles and F-16 fighters. Taiwan itself recently extended mandatory military service from four months to one year and has been revitalizing its own defense industries, including building submarines for the first time.
Although no longer increasing at the double-digit annual percentage rates of past decades, China’s defense spending has remained relatively high despite skyrocketing levels of government debt and an economy that grew last year at its second-lowest level in at least four decades.
The government says most of the spending increases will go toward improving welfare for troops. Observers say the budget omits much of China’s spending on weaponry, most of which is developed domestically after years of large-scale imports from Russia.
China’s huge capacity and Russia’s massive expenditures of artillery shells and other materiel in its war on Ukraine have raised concerns in the U.S. and elsewhere that Beijing may provide Moscow with military assistance.
Speaking at the G-20 meeting in India on Friday, U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken said that were China to engage in “material, lethal support for Russia’s aggression or were to engage in the systematic evasion of sanctions to help Russia, that would be a serious problem for our countries.”
“We’ve not seen it do that yet, but we’ve seen it considering that proposition … and I made clear that there would be consequences for engaging in those actions,” Blinken said.
China has been carrying out what it calls normal trade with Russia — including a three-fold increase in coal imports through just one border crossing, according to Chinese media — seen as providing Moscow with a partial economic lifeline alongside other countries such as India.
Beijing last month issued a proposal calling for a cease-fire and peace talks between Ukraine and Russia, but has also said it has a “no-limits friendship” with Russia and has refused to criticize Moscow’s invasion, or even to call it an invasion. It has accused the U.S. and NATO of provoking the conflict and condemned sanctions leveled against Russia and entities seen as aiding its military effort.
Last week, those sanctions were expanded to include a Chinese company known as Spacety China, which has supplied satellite imagery of Ukraine to affiliates of Wagner Group, a private Russian military contractor owned by a close associate of Russian President Vladimir Putin. A Luxembourg-based subsidiary of Spacety China was also targeted.
China, including through the NPC, has vowed to take countermeasures in response to such sanctions, and Wang said “some countries” have been “abusing extra-territorial application of their domestic laws … with the aim of taking down foreign entities and individuals and serving their own interests.”
“China stands firmly against such practices. It has introduced a number of laws and regulations to counter the containment, suppression and interference in internal affairs,” Wang said.
“For acts that undermine China’s sovereignty, security and development interests and harm the lawful rights and interests of Chinese nationals, the law contains relevant provisions to firmly counter such acts,” he said.
(AP)