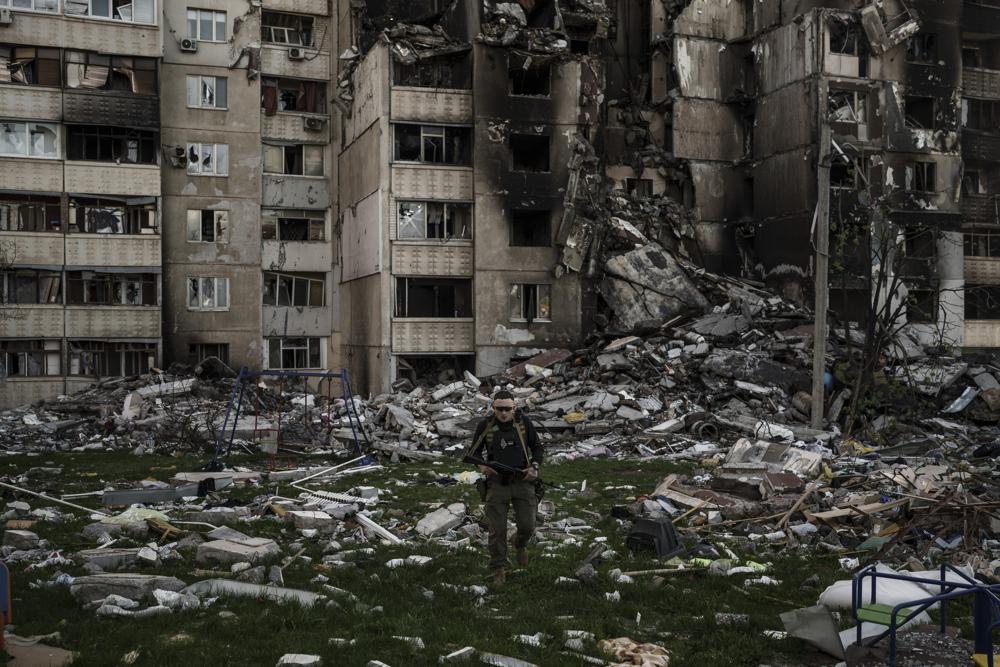
President Joe Biden asked Congress on Thursday for an additional $33 billion to help Ukraine fend off Russia’s invasion, a signal that the U.S. is prepared to mount a robust, long-term campaign to bolster Kyiv and weaken Moscow as the bloody war enters its third month with no sign of abating.
Biden’s latest proposal — which the White House said was expected to support Ukraine’s needs for five months — has more than $20 billion in military assistance for Kyiv and for shoring up defenses in nearby countries. There is also $8.5 billion in economic aid to help keep Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy’s government functioning and $3 billion for food and humanitarian programs around the world.
The assistance package, which heads to Congress for consideration, would be more than twice as large as the initial $13.6 billion in defense and economic aid for Ukraine and Western allies enacted last month that is now almost exhausted. It was meant to signify that the U.S. is not tiring of helping to stave off Russian President Vladimir Putin’s attempt to expand his nation’s control of its neighbor, and perhaps beyond.
“The cost of this fight is not cheap, but caving to aggression is going to be more costly,” Biden said. “It’s critical this funding gets approved and as quickly as possible.”
The request comes with the fighting, now in its ninth week, sharpening in eastern and southern parts of the country and international tensions growing as Russia cuts off gas supplies to two NATO allies, Poland and Bulgaria.
Biden promised that the U.S. would work to support its allies’ energy needs, saying, “We will not let Russia intimidate or blackmail their way out of the sanctions.”
Biden said the new package “addresses the needs of the Ukrainian military during the crucial weeks and months ahead” and begins a transition to longer-term security assistance that’s “going to help Ukraine deter and continue to defend against Russian aggression.”
There is wide, bipartisan support in Congress for giving Ukraine all the help it needs to fight the Russians, and its eventual approval of assistance seems certain. But Biden and congressional Democrats also want lawmakers to approve billions more to battle the pandemic, and that along with a Republican push to entangle the measure with an extension of some Trump-era immigration restrictions leaves the proposal’s pathway to enactment unclear.
Biden asked lawmakers to include an additional $22.5 billion for vaccines, treatments, testing and aid to other countries in continuing efforts to contain COVID-19, saying “we’re running out of supply for therapeutics.”
But that figure, which Biden also requested last month, seems aspirational. In a compromise with Republicans, Senate Democrats have already agreed to pare that figure to $10 billion, and reviving the higher amount would be at best an uphill fight.
Biden said he had no preference whether lawmakers combined the virus funding with the Ukraine package or split them up. “They can do it separately or together,” Biden said, “but we need them both.”
That suggested a willingness by Biden to speed passage of the Ukraine money by sidestepping the complications of tying it to the political fights over COVID-19 spending and immigration.
Biden was also asking Congress on Thursday for new powers to seize and repurpose the assets of Russian oligarchs, saying the U.S. was seizing luxury yachts and homes of “bad guys.”
He wants lawmakers to make it a criminal offense for a person to “knowingly or intentionally possess proceeds directly obtained from corrupt dealings with the Russian government,” double the statute of limitations for foreign money laundering offenses to 10 years, and expand the definition of “racketeering” under U.S. law to include efforts to evade sanctions.
Biden also asked Congress to allow the federal government use the proceeds from selling the seized assets of sanctioned Russian oligarchs to help the people of Ukraine.
In a virtual address to International Monetary Fund and World Bank leaders last week, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy called for the proceeds of sanctioned property and Central Bank reserves to be used to compensate Ukraine for its losses.
He said that frozen Russian assets “have to be used to rebuild Ukraine after the war as well as to pay for the losses caused to other nations.”
Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen said at the time that congressional action would be needed to authorize such actions.
The war has already caused more than $60 billion in damage to buildings and infrastructure, World Bank President David Malpass said last week. And the IMF in its latest world economic outlook forecast that Ukraine’s economy will shrink by 35% this year and next.
In recent weeks, the U.S. and global allies have sanctioned dozens of oligarchs and their family members, along with hundreds of Russian officials involved in or deemed to be supporting its invasion of Ukraine. The White House says the new tools will toughen the impact of the sanctions on Russia’s economy and its ruling class by making sanctions more difficult to evade.
The huge amount that Biden is seeking in the supplemental is more than half of the entire proposed $60.4 billion budget for the State Department and U.S. Agency for International Development for the next budget year, although it’s only a small fraction of the 2023 Pentagon spending plan.
According to Brown University’s Costs of War Project, the U.S. has spent about $2.2 trillion on the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq since Sept. 11, 2001. It estimates that the costs of interest by 2050 would grow to $6.5 trillion.
As a comparison, the U.S. spent $23.2 billion – including Defense, State and Homeland Security department money – in the 2001 budget year alone to cover the aftermath of 9/11 and the invasion of Afghanistan, according to the Congressional Research Service.
Of the money Biden is requesting now for military purposes, there would be $6 billion to arm Ukraine directly, $5.4 billion to replace U.S. supplies sent to the area, $4.5 billion for other security assistance for Ukraine and U.S. allies and $2.6 billion for the continued deployment of U.S. forces to the region, according to documents describing the request.
The proposed spending also has $1.2 billion to help Ukrainian refugees fleeing to the U.S. with cash assistance, English language instruction and help to school districts with Ukrainian students. There is also $500 million for American farmers to produce more wheat, soybeans and other crops for which Ukraine, a major global food supplier, has suffered decreased production.
(AP)











One Response
Nothing long-term involved. Either Putin agrees to settle and the conflict ends, or Putin decides to go nuclear and the conflict ends (within an hour or so, at most a few weeks more, at most, for those who survive the first 15 minutes).
Perhaps the use of the “long term” in the headline refers to the famous line “in the long term, we are all dead”.