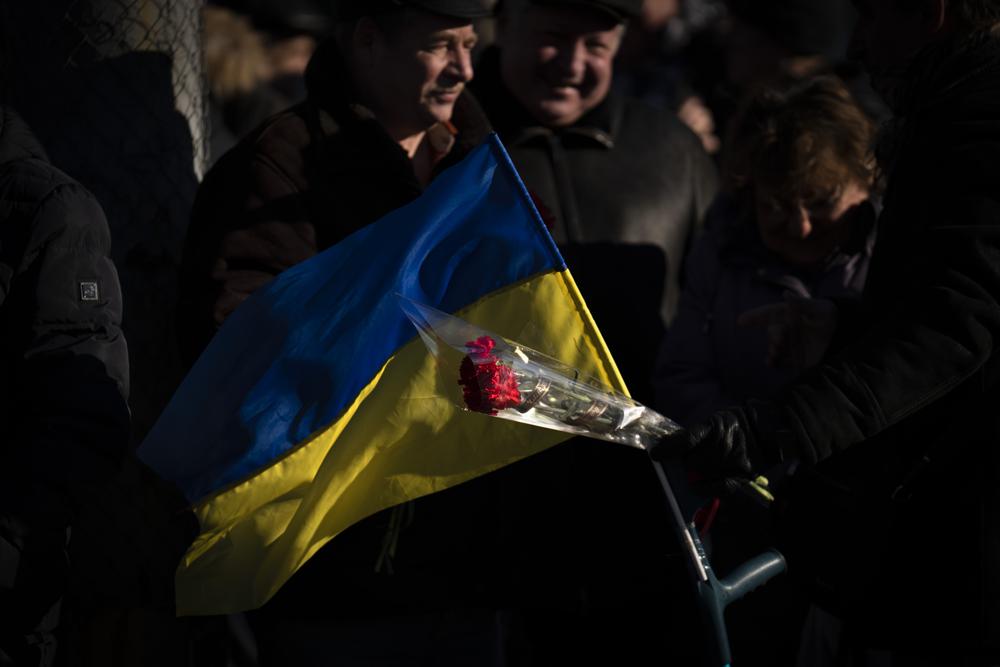
A series of cyberattacks on Tuesday knocked the websites of the Ukrainian army, the defense ministry and major banks offline, Ukrainian authorities said, as tensions persisted over the threat of a possible Russian invasion.
Still, there was no indication the relatively low-level, distributed-denial-of-service attacks might be a smokescreen for more serious and damaging cyber mischief.
At least 10 Ukrainian websites were unreachable due to the attacks, including the defense, foreign and culture ministries and Ukraine’s two largest state banks. In such attacks, websites are barraged with a flood of junk data packets, rendering them unreachable.
“We don’t have any information of other disruptive actions that (could) be hidden by this DDoS attack,” said Victor Zhora, a top Ukrainian cyberdefense official. He said emergency response teams were working to cut off the attackers and recover services.
Customers at Ukraine’s largest state-owned bank, Privatbank, and the state-owned Sberbank reported problems with online payments and the banks’ apps.
Among the attackers’ targets was the hosting provider for Ukraine’s army and Privatbank, said Doug Madory, director of internet analysis at the network management firm Kentik Inc.
“There is no threat to depositors’ funds,” Zhora’s agency, the Ukrainian Information Ministry’s Center for Strategic Communications and Information Security, said in a statement. Nor did the attack affect the communications of Ukraine’s military forces, said Zhora.
It was too early to say who was behind the attack, he added.
The ministry statement suggested Russian involvement: “It is possible that the aggressor resorted to tactics of petty mischief, because his aggressive plans aren’t working overall,” the Ukrainian statement said.
Quick attribution in cyberattacks is typically difficult, as aggressors often try to hide their tracks.
“We need to analyze logs from IT providers,” Zhora said
Oleh Derevianko, a leading private-sector expert and founder of the ISSP cybersecurity firm, said Ukrainians are always worried that such “noisy” cyberattacks could be masking something more sinister.
Escalating fears about a Russian invasion of Ukraine eased slightly as Russia sent signals Tuesday that it might be pulling back from the brink, but Western powers demanded proof.
The cyber aggression is nevertheless typical of Russian President Vladimir Putin, who likes to try to keep his adversaries off balance.
“These attacks are ratcheting up attention and pressure,” said Christian Sorensen, the CEO of the cybersecurity firm SightGain who previously worked for U.S. Cyber Command. “The purpose at this stage is to increase leverage in negotiations.”
Ukraine has been subject to a steady diet of Russian aggression in cyberspace since 2014, when Russia annexed the Crimean Peninsula and backed separatists in eastern Ukraine.
On Jan. 14, a cyberattack that damaged servers at Ukraine’s State Emergency Service and at the Motor Transport Insurance Bureau with a malicious “wiper” cloaked as ransomware. The damage proved minimal — some cybersecurity experts think that was by design, given the capabilities of Russian state-backed hackers. A message posted simultaneously on dozens of defaced Ukrainian government websites said: “Be afraid and expect the worst.”
Serhii Demediuk, the No. 2 official at Ukraine’s National Security and Defense Council, called the Jan. 14 attack “part of a full-scale Russian operation directed at destabilizing the situation in Ukraine, aimed at exploding our Euro-Atlantic integration and seizing power.”
Such attacks are apt to continue as Putin tries to “degrade” and “delegitimize” trust in Ukrainian institutions, the cybersecurity firm CrowdStrike said in a subsequent blog post.
In the winters of 2015 and 2016, attacks on Ukraine’s power grid attributed to Russia’s GRU military intelligence agency temporarily knocked out power.
Russia’s GRU has also been blamed for perhaps the most devastating cyberattack ever. Targeting companies doing business in Ukraine in 2017, the NotPetya virus caused over $10 billion in damage worldwide. The virus, also disguised as ransomware, was a “wiper” virus that scrubbed entire networks.
(AP)